Summary
Vitamin D sustains both excellent bone structure alongside immune system operation and general body health. Body production of vitamin D depends on sunlight exposure but numerous people fail to receive sufficient sunlight because of their lifestyles and geographical locations. The diet can prevent vitamin D deficiency by including foods with high vitamin D levels, such as fatty fish, together with eggs, mushrooms and fortified products. When insufficient vitamin D intake occurs, people should consider taking dietary supplements to achieve adequate levels.

In this insight, you will know about the 8 best nutritious foods that are rich in vitamin D.
Here are the list of the 8 nutritious food that are high in vitamin D
| Food | Vitamin D Content | Health Benefits |
| Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Trout, Halibut) | 526–900 IU per 3.5 oz serving | Supports bone health, immune system, and brain function |
| Small Fish (Herring, Sardines) | 214 IU per 100g | Rich in omega-3s, supports heart and brain health |
| Fish Oil (Cod Liver Oil) | 450 IU per teaspoon | Improves brain and heart health |
| Canned Tuna | 269 IU per 3.5 oz serving | Budget-friendly, convenient source of vitamin D |
| Eggs (Egg Yolks) | 37 IU per large yolk | Supports eye health, immunity, and muscle metabolism |
| Mushrooms (Exposed to UV Light) | Up to 1,110 IU per cup | Vegan source of vitamin D, supports heart health and immunity |
| Fortified Foods (Milk, Orange Juice, Cereals, Plant-based alternatives) | 100–150 IU per serving | Helps prevent vitamin D deficiency |
1. Fatty Fish
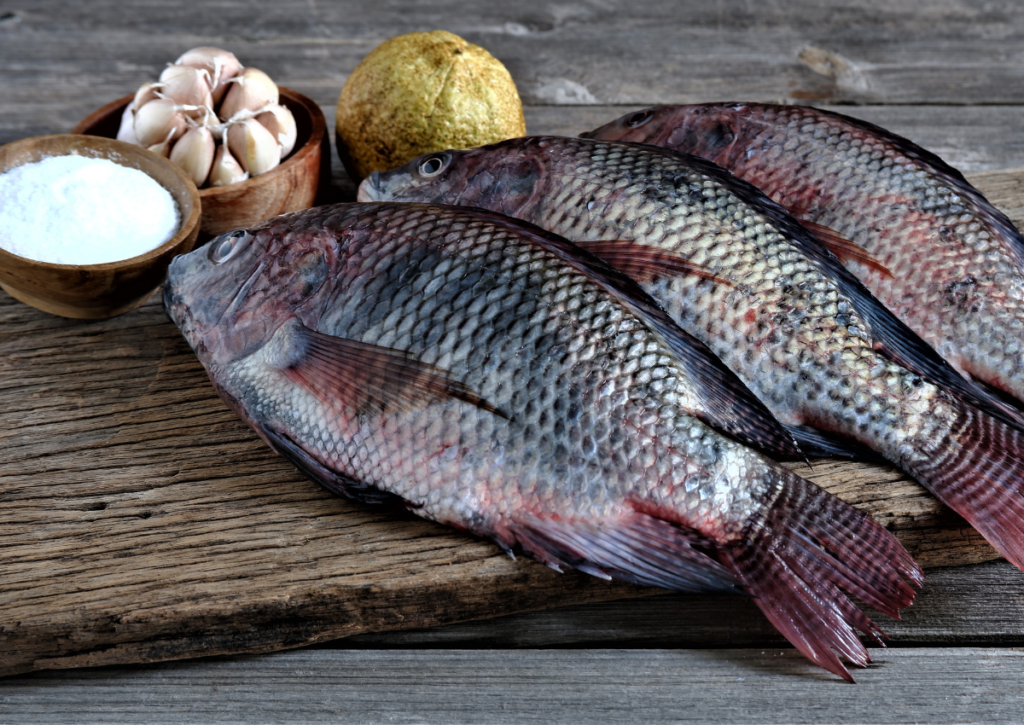

Salmon, mackerel and trout, among other fatty fish, serve as excellent sources of vitamin D for human consumption. The vitamin D content in one serving of three and a half ounces of farmed Atlantic salmon amounts to 526 IU, which accounts for 66 percent of the recommended daily intake.
Wild salmon has even greater vitamin D content than farmed salmon by delivering more than 900 IU per serving. The vitamin D content from the diet comes primarily from fatty fish, including halibut and mackerel, together with salmon.
10 Fatty Fish in India That Boost Health & Taste Amazing
The diverse fish species in India contain omega-3 fatty acids with essential nutrients that promote healthy brains and hearts while benefiting overall body health.The species of fish are commonly consumed in many traditional versions of local cuisine throughout the region.
- Indian mackerel (Bangada) serves two essential roles by benefiting heart health alongside brain wellness, although consumers usually prepare it both as curries and fried portions.
- Rohu—Rich in omega-3s, calcium, and phosphorus; popular in Bengali mustard-based gravies.
- Hilsa fish (Ilish) stands as a nutritious, heart-healthy meal in West Bengal, where people prepare it both steamed and in mustard-based sauce.
- Sardines (Mathi) – High in omega-3s, vitamin D, and calcium; often grilled or fried.
- Catla provides benefits to skin health alongside immunity enhancement and remains common as a fish ingredient in curries together with fried dishes.
- The fish known as salmon becomes a powerful anti-inflammatory agent that improves brain performance when prepared by baking and grilling methods.
- Magur (Walking Catfish)—Low in fat, high in protein; ideal for weight management and spicy curries.
- Pink Perch (Rani) functions both as a heart and skin health ally while serving as an excellent ingredient for frying along with steaming and preparing curries.
- Pomfret provides help for brain function alongside cholesterol maintenance; thus, coastal fishermen fry or grill this fish extensively.
- People use pan-fried or curry-cooked tilapia as an excellent source of lean proteins for their muscle-building needs.
2. Small Fish (Herring and Sardines)
Every 100-gram serving of fresh Atlantic herring consists of 214 IU vitamin D and presents 27% of the daily value according to recommendations. Pickled herring and canned sardines present a considerable amount of vitamin D, which makes them appropriate for individuals requiring vitamin D enhancements.
Comparing Herring and Sardines
Within the Clupeidae family, herring and sardines represent unique fish species that differ in dimensions and size, along with their diet patterns, classification approach and nutritional attributes.
Size along with weight differs between herring, which stretches to 23.6 inches but weighs 1-2.2 pounds and sardines, which measure up to 15.6 inches yet weigh 0.2-4.5 pounds.
While zooplankton and phytoplankton form the diet of these fish, herring extend their feeding habits to include marine worms.
Herring consists of species within Clupea, whereas the Sardina and Sardinops genera include the species of sardines. Some herring species exist within the Chirocentridae family along with other species.
Smoked fresh or canned versions are the available usage options for both fish species. The salt preservation method is used for herring and sardines that undergo baking to create pies.
Sardines surpass herring when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids yet contain superior protein content at 24.6 g compared to herring’s 14.2 g per 100 g and a higher calcium level of 382 mg as opposed to herring’s 77 mg. Sardines present a better eating option because they contain less mercury than other foods.
3. Fish Oil (Cod Liver Oil)
The richness of vitamin D content in cod liver oil reaches its peak concentration. A single teaspoon of this substance includes 450 IU of vitamin D to fulfill 56% of daily requirements. These vitamins and omega-3 fatty acid components of cod liver oil sustain brain wellness as well as provide heart support.
The intake of excessive cod liver oil needs to be limited because its high vitamin A concentration can harm the body at high levels.
Types of Cod Liver Oil and Fish Oil
Three distinct categories exist in the market for both cod liver oil supplements and fish oil supplements.
- Tuna and mackerel fish in daily meals deliver natural omega-3s that outperform fish oil supplements in their nutritional value.
- Fish oil supplements exist both as pure fish oil substances and combination supplements with other ingredients but typically have unappealing tastes.
- Supplementing with capsules allows patients a more convenient and more pleasant experience.
Alternatives
Vegans, along with vegetarians, can take either flax oil or algal oil supplements; both contain different omega-3 benefits compared to fish oil options.
Dosage Recommendations
Infants (0–12 months): 0.5 g
Children (1–13 years): 0.7–1.2 g
Adults (14+ years): 1.1–1.6 g
Pregnant: 1.4 g, Lactating: 1.3 g
Doctors advise consuming fish twice to thrice per week as a necessary step to obtain adequate omega-3 fatty acids.
Supplements Considerations
You should check the omega-3 content on labels to understand dosage amounts and any other supplementary ingredients present.
Food items that contain whole ingredients demonstrate better health benefits than omega-3 supplements because supplements alone might not yield optimal cardiovascular benefits.
4. Canned Tuna
Tinned tuna provides people with a budget-friendly approach to obtaining vitamin D through its convenient format. The recommended daily value for vitamin D (34% out of 800 IU) exists in 3.5 ounces of tuna, which provides 269 IU.
The mercury levels in tuna differ between light canned tuna and white tuna because white tuna possesses higher amounts. According to health professionals, patients should restrict their tuna consumption due to mercury exposure risks.
5. Eggs (Egg Yolks)
The vitamin D content in egg yolks reaches a moderate level. A single large egg yolk delivers 37 IU, which represents 5 percent of the nutritional value for this vitamin. Egg vitamin D content depends on both feed fed to the hens and the sun exposure available to them.
Pasture-raised and vitamin D-enriched feed hens lay eggs with considerably elevated vitamin D content than regular domestic hens.
Benefits:
- The anti-inflammatory proteins located in eggs help minimize gastrointestinal problems.
- Such compounds improve immune system function and decrease blood pressure levels.
- Eye health and vision problems reduction happen through the zeaxanthin and lutein contents in eggs.
- The protective effects of eggs against bacterial infections need further human-based scientific research to establish their benefits.
Nutritional Value:
You can receive the following amounts of nutrients by eating a raw egg yolk from a large-sized egg:
Calories: 55
Protein: 2.7 g
Fat: 4.51 g
Cholesterol: 184 mg
The yolk content contains significant amounts of vitamin A together with B vitamins, vitamin D and iron and zinc minerals.
Methodologies used in food preparation change nutritional details since frying adds more fat and cholesterol.
Yolk vs. Egg White:
- Egg white contains more proteins than yolk, which has only 2.7 g protein, whereas egg white provides 3.6 g protein.
- Most vitamin content, mineral elements and beneficial fats are found within the yolk.
- Tests show that consuming whole eggs yields better muscle metabolism when compared to eating egg whites individually.
- Egg yolks carry many vital nutrients but people should control their consumption amount and pick appropriate cooking techniques to get the maximum benefits from these nutrients.
6. Mushrooms
Mushrooms stand as the primary edible plant that offers vitamin D content through their natural production of vitamin D2 under sunlight exposure. Each cup of morels contains 136 IU of vitamin D, which delivers 17% of the daily value (DV). Commercial mushroom producers expose the mushrooms to UV light to increase their vitamin D content, resulting in 1,110 IU per cup.
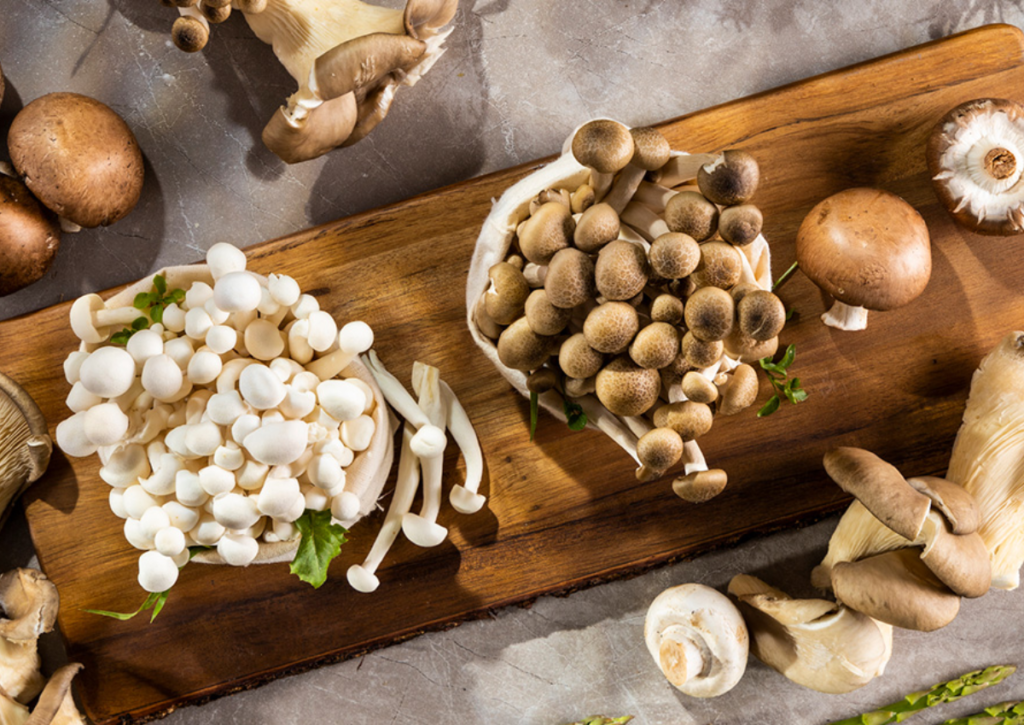

Health Benefits of Mushrooms
The nutritional value of mushrooms consists of protein together with vitamins, antioxidants and minerals, which provide a range of health advantages.
- Cancer Prevention
- The nutrients in mushrooms contain antioxidants that scientists believe can stop prostate cancer and colorectal and breast cancer development (additional studies are needed).
- Ingesting vitamin D may help protect against cancer development.
- Choline found in some foods creates uncertain effects concerning cancer development risks.
- Diabetes Management
Mushroom fiber content shows potential to decrease blood sugar levels, thus preventing type 2 diabetes development.
- Heart Health
- Video publications show that potassium functions to maintain blood pressure, thus lowering the potential of heart disease development.
- Supplements of vitamin C can decrease the possibility of developing heart disease.
- The immune compound called beta-glucans that occurs in shiitake mushrooms decreases cholesterol levels.
4. Pregnancy Benefits
Pregnant women who eat mushrooms receive necessary fetal development support through folate consumption.
5. Other Benefits
- Rich in B vitamins for energy metabolism and brain health.
- The body needs choline because it enables proper movements of muscles, maintains nerves and supports memory functions.
- The only vegan, non-fortified source of vitamin D.
- Mushrooms provide necessary minerals to the diet through their content of selenium and copper as well as iron and phosphorus.
The healthy nutritional value in mushrooms makes them beneficial for every diet since they help maintain wellness along with health.
7. Fortified Foods

Fortified products serve as nutritional supplements that replace vitamin D deficiencies in diets because natural food sources remain minimal.
Common fortified foods include:
- Milk and plant-based alternatives (almond, soy, oat) – about 100-150 IU per cup
- Orange juice—100 IU per cup
- Breakfast cereals—40-100 IU per serving
A portion of vitamin D varies by brand throughout yogurt and cheese products.
Fortified vs. Enriched Foods:
The manufacturing process of fortified foods includes adding essential nutrients that were previously absent (for example, vitamin D appears in milk).
After food processing, manufacturers restore vitamins such as folic acid to wheat flour, which makes the foods enriched.
Health Benefits and Risks:
Through fortification, medical professionals have diminished nutrient deficiency-related diseases to decrease rickets incidence.
Children face particular risks when they consume too many fortified food products due to potential harmful overdoses of vitamin and mineral content.
Fortified foods normally undergo processing, which results in products with excessive amounts of sugar, fat and sodium.
For Children:
The nutritional advantages of fortified foods help children reach their nutritional goals, although several children consume unsafe amounts of vitamin A, zinc and niacin.
It is essential for parents to review both serving sizes and the nutrient contents of the food labels.
For Adults:
- The majority of adults fulfill their basic nutritional needs while being deficient in calcium alongside magnesium and fiber and some vitamins.
- Vegans and residents of specific diets receive improved nutrition from fortified foods.
- Older adults, together with pregnant women, face health complications when they consume too much vitamin A, which also includes pregnant females.
- The Federal Drug Administration regulations for daily nutrient intakes remain outdated; thus, they might present unsafe recommended consumption limits.
8. Cheese
The nutritional value of cheese includes vitamin D together with additional essential vitamins. The food product comprises phosphorus together with fat, protein, vitamins and calcium in addition to vitamins. Raw consumption of this item is possible but you can also use it to add taste to your salads.
Health Benefits of Cheese
Nutritional Benefits:
Tree nuts, along with cheese, offer several important components, including calcium and protein, together with fat and vitamins A and B12, as well as zinc and phosphorus and riboflavin. The ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in grass-fed cheese delivers possible health advantages for both heart systems and metabolic operations.
Dental Health:
Danish research revealed children who consumed more dairy products developed fewer dental cavities, according to studies about the protective benefits cheese provides to teeth.
Heart Health & Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
The fermentation process in dairy products generates cheese, which helps manage heart diseases and anti-inflammatory responses. High-fat cheeses contain conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) that helps prevent obesity and defends the body against heart diseases.
Health Risks:
Contamination Risks:
Raw health risks come from soft cheeses based on unpasteurized milk, including Brie, along with Camembert and blue cheese, because they harbor listeria that affects pregnant women along with infants, while both the elderly and people who have compromised immune systems remain at risk.
High in Calories, Fat, and Sodium:
The high calorie content in cheese combines with saturated fats and too much sodium, which makes this food dangerous for people who struggle with pressure or cholesterol regulation. The absence of fiber in cheese leads to potential constipation problems.
Lactose Intolerance & Milk Allergies:
With age, the lactose content of cheeses decreases, which benefits those who suffer from lactose intolerance yet moderate digestive symptoms might still occur. Those who have a milk allergy need to stay away from all types of cheese since their bodies produce adverse responses to dairy proteins.
Types of Cheese:
People who do not need to worry about heart conditions should consume this choice.
Low-Fat/Reduced-Fat: Contains less fat, ideal for heart-conscious diets.
Both cheddar and Swiss, together with Parmesan, make up aged cheeses that present a firm texture along with distinct robust flavors.
Fresh Cheeses: Includes ricotta and cottage cheese; soft and high in moisture.
Why You Need Vitamin D
The key functions of vitamin D depend heavily on these three major processes:
Healthy bones depend on vitamin D because it facilitates the absorption of calcium, which shields against osteoporosis along with rickets and avoids bone fractures.
The immune system benefits from vitamin D to operate more effectively, thus decreasing exposure to infections and autoimmune.
When present in the body, vitamin D shows associations with reduced occurrences of depression along with mood disorders.
Homeostasis of blood pressure along with regular arterial function helps lower the probability of heart disease.
Insufficient vitamin D affects muscle strength, which raises the danger of physical accidents.
Tips to Increase Vitamin D Intake
Irradiate your body with sunlight for no less than 10 minutes up to 30 minutes throughout sunny midday periods multiple times each week based on your skin type and geographical area.
People should include meals containing vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish and eggs and fortified products regularly.
Some patients require supplements according to doctor recommendations when sun exposure and food meals alone fail to achieve vitamin D requirements.
What foods are highest in vitamin D?
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna have the most vitamin D. Fish liver oil is also a great source. Smaller amounts are found in egg yolks, cheese, and beef liver. Some mushrooms have vitamin D2, and certain store-bought mushrooms have even more because they are exposed to extra sunlight.
How to Quickly Boost Your Vitamin D Levels ?
Here are three simple ways to increase your vitamin D:
- Eat foods rich in vitamin D, such as fish, milk, cereals, and orange juice.
- Spend some time in the sun daily to help your body produce vitamin D.
- Take a vitamin D3 supplement or cod liver oil.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D?
You can get vitamin D from these foods:
- Oily fish—like salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel.
- Red meat—a good natural source.
- Liver—but avoid it if you’re pregnant.
- Egg yolks—a simple and easy option.
- Fortified foods—such as certain spreads and breakfast cereals.
What are the signs of low vitamin D?
Not getting enough vitamin D can cause:
- Muscle pain
- Bone pain
- More sensitivity to pain
- Tingling in hands or feet (like “pins and needles”)
- Muscle weakness (especially in the upper arms or thighs)
- Walking with a waddle (due to weak hip or leg muscles)
Does omega-3 contain vitamin D?
Fish oil is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, but it doesn’t have as much vitamin D as cod liver oil.
Which Fruits Have High Vitamin D?
Looking for fruits rich in vitamin D? Here are some top choices:
- Bananas—Eating 1 to 2 bananas daily is recommended by health experts. They are a good option for maintaining overall health.
- Figs (Anjeer) – Known as a “heavenly fruit,” figs are packed with vitamins D, C, A, and B, making them a great addition to your diet.
Which dry fruits are rich in vitamin D?
Looking for dry fruits that have vitamin D? Here are seven options:
- Dried Apricots—They provide about 1.5 IU of vitamin D per 100 grams.
- Dried Figs—These contain around 3 IU of vitamin D per 100 grams and are also rich in fiber, calcium, and potassium.
- Almonds—A nutritious option with many health benefits.
- Raisins—A tasty and healthy snack.
- Prunes—Good for digestion and overall health.
- Dates—A naturally sweet source of nutrients.
- Cranberries—Packed with antioxidants and vitamins.
Vitamin D is essential for strong bones, immunity, and overall health. While sunlight is a natural source, many people don’t get enough. Incorporate these 8 vitamin D-rich foods into your diet:
Stay proactive about your health by making vitamin D a priority in your diet!
Discover the top 8 nutritious foods packed with vitamin D! 🌞 Boost your health with the right diet. Prioritise your well-being and make smart food choices today. Read more on Glance Insight!
What foods are highest in vitamin D?
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna have the most vitamin D. Fish liver oil is also a great source. Smaller amounts are found in egg yolks, cheese, and beef liver. Some mushrooms have vitamin D2, and certain store-bought mushrooms have even more because they are exposed to extra sunlight.
How to Quickly Boost Your Vitamin D Levels ?
Here are three simple ways to increase your vitamin D:
Eat foods rich in vitamin D, such as fish, milk, cereals, and orange juice.
Spend some time in the sun daily to help your body produce vitamin D.
Take a vitamin D3 supplement or cod liver oil.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D?
You can get vitamin D from these foods:
Oily fish
Red meat
Liver
Egg yolks
Fortified foods
What are the signs of low vitamin D?
Not getting enough vitamin D can cause:
Muscle pain
Bone pain
More sensitivity to pain
Tingling in hands or feet (like “pins and needles”)
Muscle weakness (especially in the upper arms or thighs)
Walking with a waddle (due to weak hip or leg muscles)
Does omega-3 contain vitamin D?
Fish oil is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, but it doesn’t have as much vitamin D as cod liver oil.
Which dry fruits are rich in vitamin D?
Dried Apricots
Almonds
Raisins
Prunes
Dates
Cranberries